Abstract
Background:
As the most common subtype of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) accounts for approximately 38% of NHL cases in China. Rituximab plus chemotherapy (R-chemo) is widely used by Chinese physicians as the standard of care for patients with DLBCL. The benefits of R-chemo have been well demonstrated in many randomized clinical trials. However, the safety and effectiveness of R-chemo in real clinical setting need to be further investigated.
Methods:
This study was a multicenter, prospective, single-arm observational study conducted in China. DLBCL patients who were eligible to receive R-chemo (CHOP or non-CHOP) as first-line treatment were enrolled with no specific exclusion criteria. Individual dose and duration of treatment was determined at the investigator's discretion, local labeling information and standard clinical practice. Data on safety and effectiveness were collected from medical records. Patients went through safety and effectiveness assessment after the last rituximab dose was administered, and then followed-up for 3 years. The safety endpoints included adverse events (AEs), severe adverse events (SAEs), adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and adverse events of special interest (AESIs). The effectiveness endpoints included overall response rate (ORR), complete response (CR), unconfirmed CR (CRu), partial response (PR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). This study was registered in clincialtrials.gov (NCT01340443).
Results:
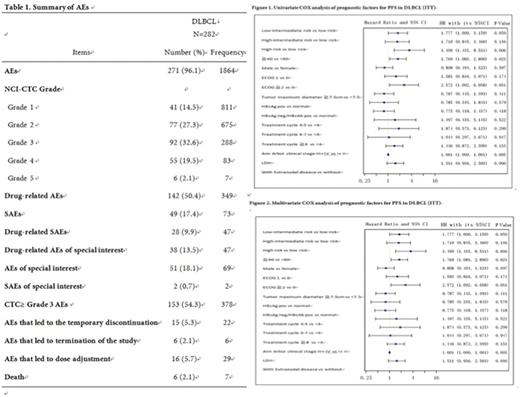
In total, 282 DLBCL patients received at least one dose of rituximab. During the study, 271 (96.1%) patients reported 1864 AEs (Table 1). The common drug-related AEs (incidence ≥ 5%) in DLBCL patients were white blood cell count decreased (16.0%), lung infection (6.4%), neutrophil count decreased (5.7%), and infusion related reaction (5.3%). Drug-related AEs of special interest in DLBCL patients were infusion related reactions (6.4%), others (2.5%), other opportunistic infections (1.8%), hypogammaglobulinaemia (1.4%), serum sickness and serum sickness symptoms (1.1%), hepatitis B virus reactivation (0.7%), and prolonged neutropenia (0.4%). Six (2.1%) DLBCL patients died due to AEs. The cause of death included lung infection (2 cases), acute leukemia (1 case), cardiac failure (1 case), acute left ventricular failure (1 case), sepsis (1 case), and multiple organ failure (1 case). Of which, 1 patient died of sepsis and lung infection.
Effectiveness assessment was performed in intention to treat (ITT) population, comprising patients who received at least one cycle of rituximab and completed at least one tumor assessment after baseline. Among 258 DLBCL patients in ITT population, the overall response rate were 94.2% [95% CI (90.59%, 96.71%)], and CR, CRu, PR, and stable disease (SD) were 55.0%, 18.2%, 20.9%, and 5.8%, respectively. Subgroup analysis showed that ORR was statistically different in ECOG, IPI, tumor maximum diameter, extra nodal, age, type of hepatitis B, site and total treatment cycles in DLBCL patients. The 2-year PFS rate was 68% (60%, 74%) for DLBCL patients. The COX univariate analysis showed that IPI ,age ,ECOG and LDH were statistically different for PFS while gender, tumor maximum diameter, type of hepatitis B, rituximab treatment cycle, Ann Arbor stage and extra nodal involvement showed no statistically different, while age , ECOG and LDH remained statistically different for PFS for the possible reason of correlation between these factors and short follow-up time in this non-intervention study(Figure 1,2). The average rituximab treatment cycles for early stage (Ann Arbor I+II) and late stage(Ann Arbor III+IV) were 5.6 and 5.9 respectively.
Summary and conclusion:
Overall, R-chemo as the first-line treatment of DLBCL was well tolerated by patients in China. The effectiveness in real-life clinical practice was consistent with previous studies. This study provides long term safety data and insights into treatment responses and prognostic factors in Chinese patients with DLBCL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal